In the teacher training programmes in art education (grammar/secondary schools), students develop an independent artistic and art education approach by combining artistic practice, art education, art didactics and art studies. They acquire skills and abilities that prepare them for future professional practice as art teachers.
Art is studied as one of two subjects at the BURG. The other subject - as well as the 'Bildungswissenschaften' educational sciences - must be studied at Martin Luther University (MLU).
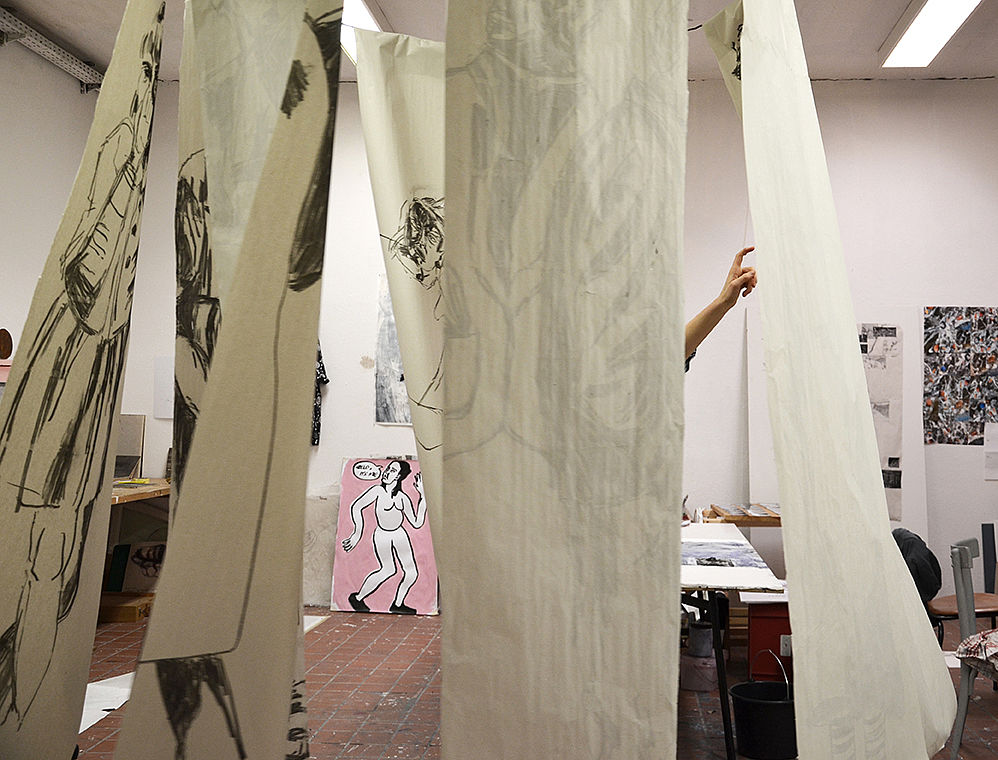
In the first year of study, known as the BURG year, students primarily study the basics of visual arts and art studies and do not yet attend any courses at MLU. At the BURG, studio work (artistic practice) takes place in two classes, with a choice of specialisation in ‘Bildhauerische und performative Praxis' Sculptural and Performative Practice or ‘Malerische und grafische Praxis' Painting and Graphic Practice. While participation in artistic practice classes is optional in the first two semesters, intensive artistic practice in the studios begins in the third semester and forms a central part of the degree programme. Students choose one of the two classes by attending selected events (e.g. plenum) during the BURG year and exchanging ideas with fellow students in the classes.
Their own artistic experiences also play a role in art education experiments, in close connection with art education concepts and academic reflections. References are made to questions of contemporary art, everyday and media cultures as well as social developments.
In the third semester, students attend an introductory seminar in art education, which is followed by courses in art education/art didactics as well as practical school exercises and two school internships. Courses in art studies and excursions are offered every semester.
The standard period of study for art (grammar school teaching degree) is 10 semesters, for art (secondary school teaching degree) 9 semesters. The study structure for both programmes is largely comparable. The two degree programmes differ in the proportion of artistic practice and the number of credit points to be obtained here. In the specialised didactic courses, a distinction is made between the different types of school with regard to considerations on lesson planning and learning groups.